Everything about solar inverters and their types
Have you ever wondered why we can't directly connect solar panels to electronic devices and operate them? If yes, then you have come to the right place. In this article, we will try to answer questions about the need for solar inverters, the difference between regular and solar inverters, the various types of inverters, besides answering why we can't directly attach solar panels to our electrical appliances.
What’s Ahead?
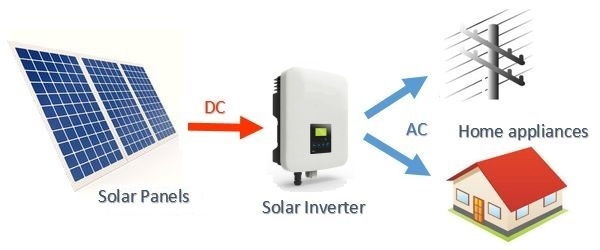
Why do we need an inverter?
The basic function of an inverter is to convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). Direct current is generally produced by batteries, photovoltaic (PV) cells, fuel cells, etc. Large scale production of electricity takes place in the form of alternating current everywhere as the transmission cost for direct current is very high. For this reason, all the devices that we use in our daily lives operate on an alternating electric supply. Thus, an inverter is needed to convert DC into AC so that it can be used to operate appliances and electronics.
Regular inverter Vs Solar inverter
The basic function of a regular inverter and a solar inverter is the same; they both convert direct current into alternating current. A regular inverter or home UPS takes DC stored in batteries and converts it into AC. Similarly, a solar inverter also converts the direct current produced by PV cells of solar panels into AC. The only difference between a solar inverter and a regular inverter is that the latter always takes input from a storage battery whereas the former can be connected to solar panels, solar batteries, or even the main electricity grid depending on its type. Thus, while a regular inverter must be connected to a battery, a solar inverter has no such mandatory requirement. Solar inverters are also the point of monitoring for the system and the solar monitoring device is attached to the solar inverter.
Solar Management Unit (SMU)

SMU is a device that can be used to convert a regular inverter into a solar inverter. It has a switch that can be used to choose between the two modes except during the night when it acts as a regular inverter only after stored battery energy has been consumed. An SMU has a charge controller and it also prioritizes solar power over grid power to boost savings. SMU also optimizes charging cycles to improve battery health and performance.
Types of solar inverters

Firstly, there are string inverter systems and microinverter systems. In a string inverter system, all the solar panels in the solar power unit are connected with each other and the cumulative electricity generated by them is brought to the inverter which then converts DC to AC.
Microinverters
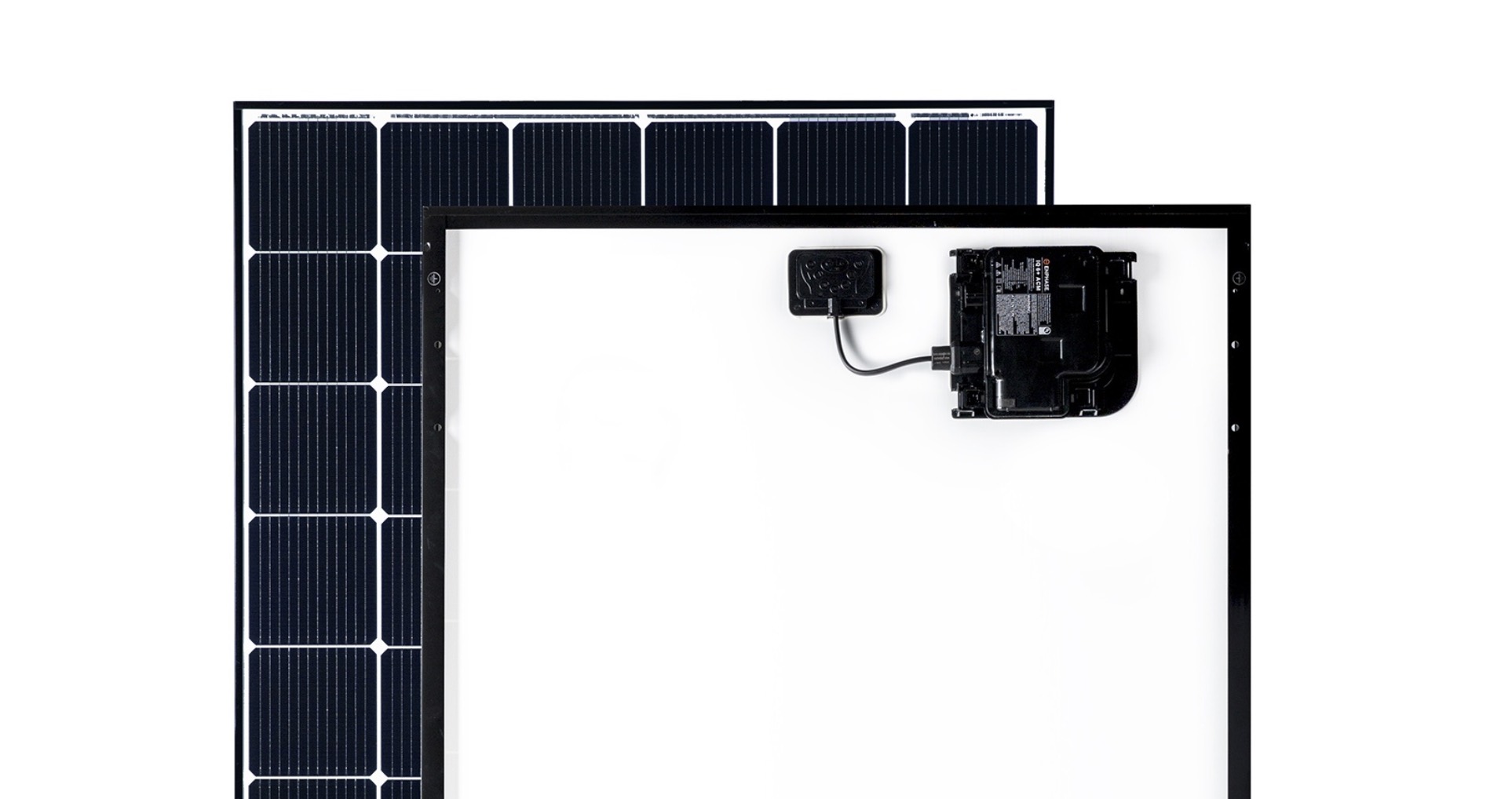
In a microinverter system, individual panels are attached with a microinverter that converts the electricity generated by the panel into AC before sending it for use. Microinverters have a higher upfront cost but their benefits easily make up for that. In the case of partial shading of solar panels in a solar array, microinverters ensure that the output of unshaded panels does not get affected. This is made possible because every panel has its own micro-inverter as opposed to a string system in which the power output of individual panels is determined by the panel with the least power generation. Thus, microinverters should be the first choice at places where there are chances of partial shading or panels have different tilt angles or face different directions.
Besides these, there are off-grid, on-grid, and hybrid inverters depending on the connectivity type of solar inverter with the main electricity grid. Let’s discuss them in detail.
Off-Grid Solar Inverter
%20(2)1605124993199.png?alt=media&token=b7e13b90-b6ee-4564-a94f-fe1dc34e47a4)
An off-grid solar power system is one that is not connected to the main electricity grid. It is a standalone power unit where all the electricity generated by the solar panels is consumed at the place of installation of the solar module and there is no alternative electricity source. For this reason, it is also called Stand Alone Power System (SAPS). An off-grid solar inverter, thus, is a solar inverter that forms a part of an off-grid solar power unit.
An off-grid solar inverter is connected to a solar battery and has a mains charger and solar charge controller built-in. The mains charger charges the solar battery while simultaneously AC is being supplied to the household. The role of a charge controller is two-fold.
- Firstly, they prevent the overcharging of solar batteries from the solar array during the daytime.
- Secondly, they prevent the reverse migration of charge from the battery to the solar panel during night time.
The best type of charge controller to use is an MPPT charge controller, where MPPT stands for maximum power point tracking. The other type of charge controller is Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) but it is not as efficient as MPPT ones.
On-Grid Solar Inverter

Also called grid-tied solar inverters, on-grid solar inverters convert DC generated by solar panels to AC and send back the excess power generated to the main grid through a net-metered connection. There is no battery in an on-grid inverter system and it is directly connected to the solar panels and the main grid. On-grid inverters step up the voltage of the current using an inbuilt transformer so that it matches the voltage of the supply line.
It also immediately disconnects from the grid in case the main grid goes down or if there is a blackout to ensure that no worker on the mainline suffers an electric shock. Additionally, users can install a zero-export device that can be used to regulate the amount of solar electricity being sent to the main grid, or even cut-off the export to the grid completely.
Hybrid Solar Inverter
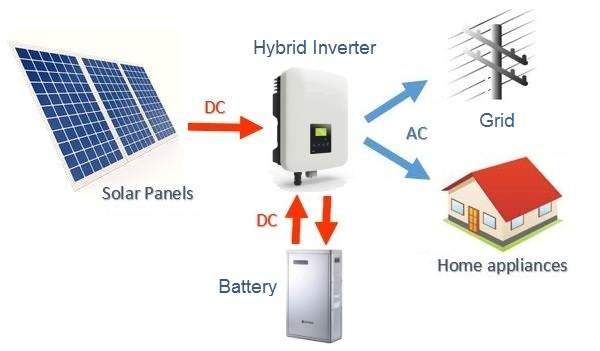
Hybrid solar inverters get their name because they incorporate the features of both an off-grid inverter as well as those of an on-grid inverter. Thus, a hybrid inverter is connected to both the main grid as well as a solar battery. It also has a charge controller built in to regulate the charging of the solar battery. The first priority of a hybrid solar system is to supply solar electricity to power the house or business they are set upon. After that, the second priority is to charge the solar battery from solar power so that there is stored solar electricity for times when the solar panels are unable to meet the energy requirement. Once the solar battery is fully charged and the household electricity demand is met, the hybrid solar inverter steps up the voltage of solar electricity and sends the excess to the grid which helps the solar owner earn revenue or credit points.
 Unergia
Unergia